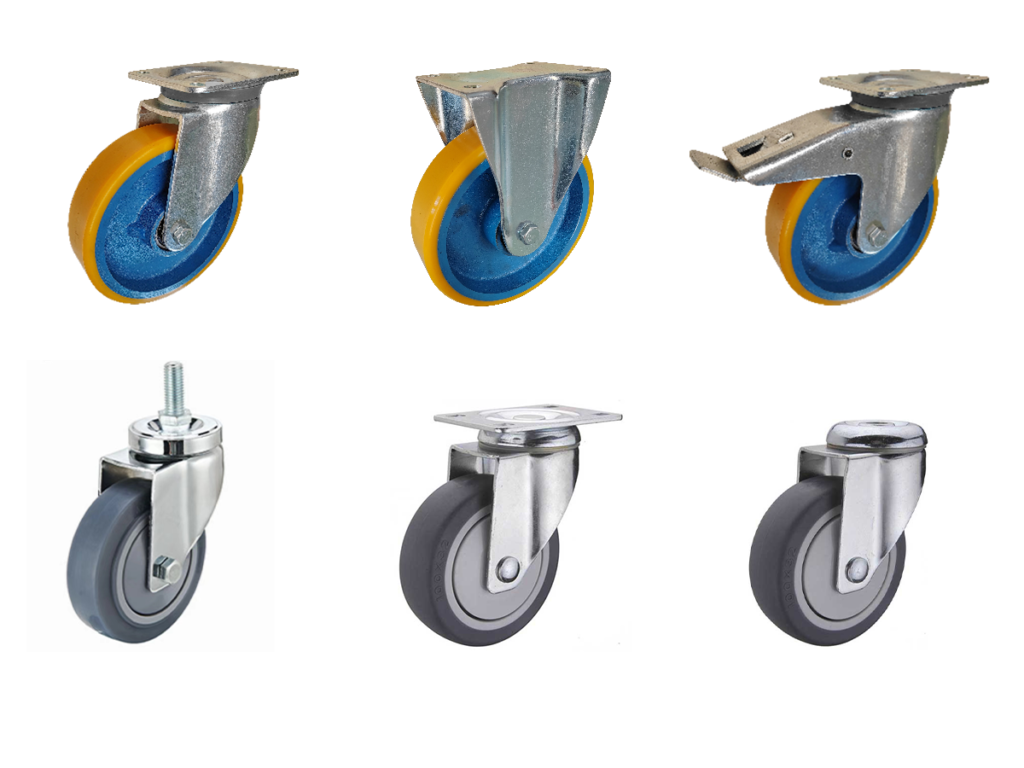
Using caster wheels can greatly enhance the mobility of your equipment, making it easier to transport items across various surfaces. But with so many types of caster wheels available, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of caster wheels, their materials, and their specific uses to help you make an informed decision.
Caster wheels come in various types such as fixed, swivel, and braked casters. They are made from materials like rubber, polyurethane, nylon, aluminum, cast iron, forged steel, pneumatic wheels, and foam wheels, each suited for different environments. Factors like wheel dimensions, load capacity, and floor compatibility play crucial roles in selecting the right caster wheel for your needs.
Let’s delve deeper into the different types and their specific features to understand what suits your requirements best.
Maneuverability: Fixed Casters, Swivel Casters, and Braked Casters
| Type | Features | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Casters | Movement in a straight line, stability and control | Industrial settings, heavy machinery |
| Swivel Casters | 360-degree rotation, enhanced maneuverability | Office chairs, shopping carts, hospital beds |
| Braked Casters | Braking mechanism for locking the wheel | Medical equipment, workstations |
Fixed Casters

Fixed casters are designed to allow movement in a straight line, providing stability and control. These casters are typically used in applications where directional control is crucial, such as in industrial settings with heavy machinery or equipment that needs to move in a straight path without deviating. Fixed casters are robust and can handle significant weight, making them ideal for heavy loads that require steady and controlled movement.
Swivel Casters
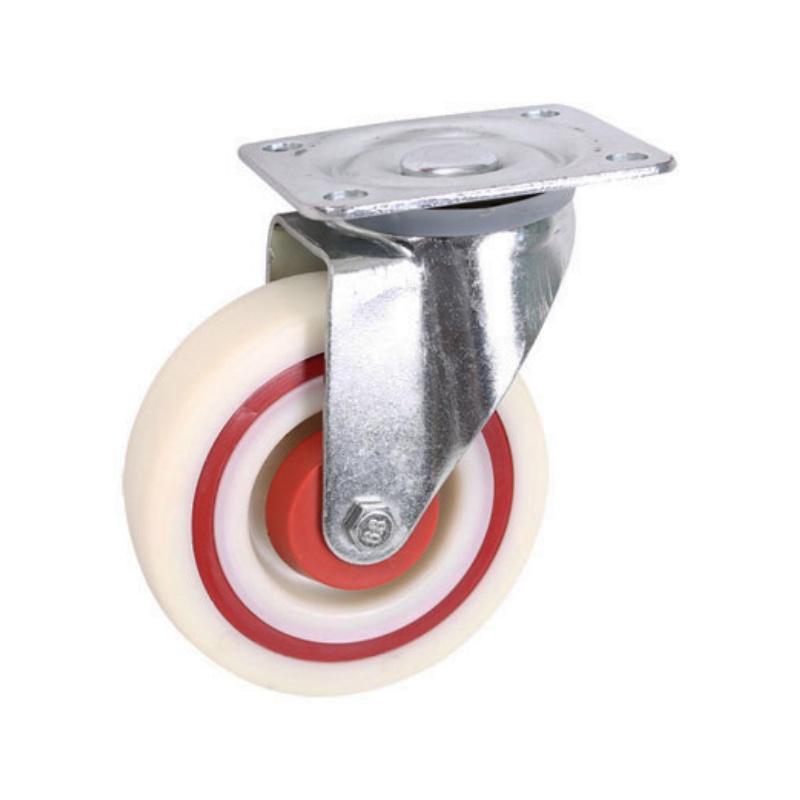

Swivel casters offer 360-degree rotation, which enhances maneuverability. This feature allows the wheels to pivot and change direction easily, making them perfect for navigating tight spaces or areas with obstacles. Swivel casters are commonly used in applications such as office chairs, shopping carts, and hospital beds, where ease of movement in multiple directions is essential. The ability to rotate freely reduces the effort needed to move equipment, improving efficiency and reducing strain on users.
Braked Casters
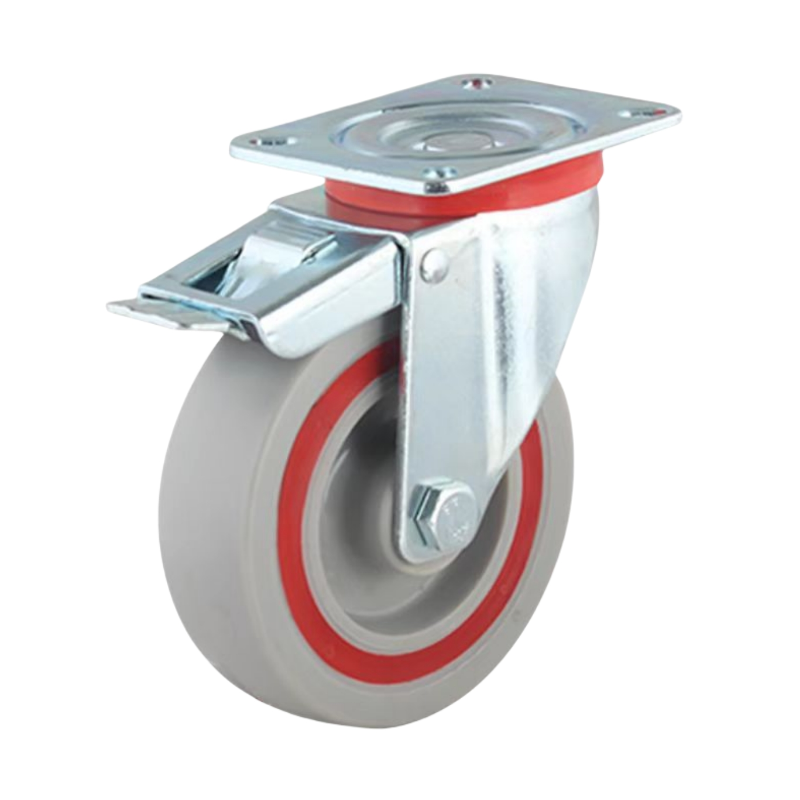

Braked casters come with a braking mechanism that locks the wheel in place, ensuring safety and stability when the equipment is stationary. These casters are particularly useful in scenarios where stability is critical, such as on medical equipment, workstations, or any mobile apparatus that needs to stay securely in place during use. The brake can be engaged or disengaged easily, providing both mobility and stability as needed.
Caster Wheel Materials
| Material | Properties and Benefits | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Shock absorption, quiet operation | Indoor applications, hospitals, libraries |
| Polyurethane | Durable, chemical-resistant, non-marking | Industrial, commercial environments |
| Nylon | High temperature and chemical resistance | Chemical processing plants, cleanrooms |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Food processing plants, outdoor applications |
| Cast Iron | Extremely durable, handles very heavy loads | Industrial environments, warehouses |
| Forged Steel | Highest load capacity, extreme durability | Foundries, steel mills |
| Pneumatic | Air-filled, excellent shock absorption | Outdoor use, construction sites |
| Foam | Puncture-proof, good shock absorption | Landscaping, outdoor utility carts |
Rubber Wheels
Rubber wheels are known for their excellent shock absorption and quiet operation. They are ideal for indoor applications where noise reduction is important, such as in hospitals, libraries, and office buildings. Rubber wheels provide good traction and are gentle on floors, reducing the risk of damage to surfaces.
Polyurethane Wheels
Polyurethane wheels offer a balance between durability and floor protection. They are resistant to chemicals, oils, and abrasions, making them suitable for industrial and commercial environments. Polyurethane wheels are non-marking and can handle heavier loads compared to rubber wheels, making them ideal for warehouses, factories, and retail settings.
Nylon Wheels
Nylon wheels are versatile and can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments. These wheels are perfect for use in areas where chemical resistance is needed, such as in chemical processing plants or cleanrooms. Nylon wheels are also non-marking, which means they won’t leave traces or damage floors, making them suitable for a wide range of surfaces.
Aluminum Wheels
Aluminum wheels are lightweight yet strong, offering excellent resistance to corrosion. They are commonly used in environments where exposure to moisture or chemicals is frequent, such as in food processing plants or outdoor applications. Aluminum wheels provide a smooth ride and are suitable for medium to heavy loads.
Cast Iron Wheels
Cast iron wheels are extremely durable and can handle very heavy loads. They are best suited for industrial environments with rough surfaces, such as warehouses and factories. Cast iron wheels are resistant to wear and tear, but they can be noisy and may damage delicate floors, so they are typically used in areas where floor protection is not a primary concern.
Forged Steel Wheels
Forged steel wheels offer the highest load capacity and durability. They are used in the most demanding industrial applications where heavy-duty performance is required, such as in foundries, steel mills, and other heavy manufacturing environments. Forged steel wheels can withstand high impact and extreme conditions but require smooth, hard surfaces to operate effectively.
Pneumatic Wheels
Pneumatic wheels are filled with air, providing excellent shock absorption and a smooth ride over rough or uneven surfaces. They are ideal for outdoor use, such as on carts and equipment used in construction sites, agriculture, and landscaping. Pneumatic wheels are also gentle on floors and reduce vibrations, making them suitable for delicate cargo.
Foam Wheels
Foam wheels are similar to pneumatic wheels but are filled with foam instead of air. This makes them puncture-proof and maintenance-free while still offering good shock absorption. Foam wheels are ideal for applications where a smooth ride is needed, but the risk of punctures is high, such as in landscaping or outdoor utility carts.
Wheel Dimensions
Choosing the correct wheel dimensions, including diameter and width, is crucial for load distribution and maneuverability. Larger wheels typically offer better performance on uneven surfaces and can carry heavier loads, while smaller wheels are more suited for lighter loads and smooth surfaces. The width of the wheel also affects stability; wider wheels provide better weight distribution and stability, making them ideal for heavy or bulky equipment.
Wheel Material Related to Floor Compatibility
| Material | Finished Wood Floor | Concrete Floor |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Excellent | Good |
| Polyurethane | Excellent | Excellent |
| Nylon | Good | Excellent |
| Aluminum | Fair | Excellent |
| Cast Iron | NR (Not Recommended) | Excellent |
| Forged Steel | NR (Not Recommended) | Excellent |
| Pneumatic | Excellent | Good |
| Foam | Excellent | Good |
Understanding Floor Compatibility
Make sure the wheel material is compatible with the floor surface. This is important to prevent damage and ensure the wheels roll smoothly. For example, if you have a finished wood floor, you want to use a softer material like rubber or polyurethane. These materials give you good traction and protect the floor from scratches. On the other hand, if you have a wood floor, you don’t want to use a harder material like cast iron or forged steel. However, cast iron and forged steel wheels work great on concrete floors. They’re durable and can handle heavy loads. When you match the wheel material to the type of floor, you’ll extend the life of the wheels and the floor. Plus, you’ll make the equipment easier and safer to move.
Caster Load Capacity
Selecting casters based on weight capacity is critical to ensure safe and efficient operation. Casters come in different load capacities:
| Load Capacity | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Light Duty | Suitable for loads up to 500 lbs | Office furniture, lightweight carts, small appliances |
| Medium Duty | Designed for weights between 501 and 2,000 lbs | Hospital beds, larger carts, moderate industrial equipment |
| Heavy Duty | Can handle loads over 2,000 lbs | Heavy machinery, industrial transport equipment |
Understanding the load capacity helps in choosing the right caster that can handle the expected weight without failure.
Caster Mount Type: Plate, Stem, and Bolt Hole
| Mount Type | Features | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Plate Mounts | Larger surface area for mounting, suitable for heavy loads | Industrial equipment, large carts, heavy machinery |
| Stem Mounts | Easy to install and remove, ideal for furniture and lighter equipment | Medical equipment, retail displays |
| Bolt Hole Mounts | Flexible installation, suitable for various applications | Modular equipment, display stands |
Plate Mounts

Plate mounts provide a larger surface area for mounting, making them suitable for heavy loads. The plate is usually attached to the bottom of the equipment with screws or bolts, providing a secure and stable connection. This type of mount is ideal for industrial equipment, large carts, and heavy machinery that require robust support.
Stem Mounts

Stem mounts are easy to install and remove, making them ideal for furniture and lighter equipment. The stem fits into a socket or hole in the equipment, secured with a clip or nut. This mounting type allows for quick changes and adjustments, which is useful for applications where mobility and flexibility are needed, such as in medical equipment or retail displays. Stem mounts come in various designs, including threaded stems, grip ring stems, and expanding stems, each providing a different method of attachment depending on the specific needs of the equipment.
Bolt Hole Mounts

Bolt hole mounts offer flexibility in installation, suitable for various applications. The caster is attached through a single bolt or screw, allowing for easy adjustments and replacements. This type of mount is commonly used in situations where the caster needs to be frequently removed or adjusted, such as in modular equipment or display stands. Bolt hole mounts are also advantageous in applications where space is limited, as they require less mounting area compared to plate mounts.
Summary
In conclusion, choosing the right caster wheel involves understanding your specific needs and matching them with the appropriate type of caster, material, and mounting option. Whether you need maneuverability, load capacity, or specific material compatibility, there’s a caster wheel designed to meet your requirements. Make sure to consider all these factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your equipment.
When selecting caster wheels, remember to:
- Identify the Type of Caster: Determine if you need fixed, swivel, or braked casters based on the maneuverability and control required for your application.
- Choose the Right Material: Select a material that matches the environment and floor type where the caster will be used. Consider factors such as chemical resistance, noise reduction, and load capacity.
- Evaluate Wheel Dimensions: Choose the appropriate wheel diameter and width to ensure proper load distribution and ease of movement on your specific surface.
- Check Load Capacity: Ensure the casters can handle the expected weight to avoid failures and maintain safety.
- Select the Mount Type: Decide between plate, stem, or bolt hole mounts based on the ease of installation, stability, and specific mounting requirements of your equipment.
By taking these factors into account, you can select the most suitable caster wheels that will enhance the mobility, efficiency, and safety of your equipment.